Mobile commerce (m-commerce) created major changes to digital market shopping activities while transforming payment systems. Organizations shifted their platforms and services to mobile accessibility because smartphone internet usage is steadily rising.
By 2025 mobile-commerce will represent 72.9% of all e-commerce sales across the world. AI-based recommendations together with mobile payment solutions have transformed the buying habits of consumers and research indicates the mobile payment market will exceed $12.06 trillion by 2027.
This blog will explore the development of m-commerce focusing on current transformations, benefits and future.
What is mobile commerce?
Mobile commerce, also known as "m-commerce", is the process of buying and selling goods and services through mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, essentially allowing users to shop online directly from their mobile
Examples: Users who use smartphones to purchase items through online shopping platforms like Daraz, and Amazon, and complete their bookings through Airbnb are some of the popular examples of mobile commerce. These platforms allow users to make transactions smoothly, securely, and quickly without requiring a desktop computer.
How does mobile commerce work?
User convenience becomes possible through mobile commerce because it establishes simplified operational processes. Mobile banking functions as the key component of mobile commerce to offer secure transaction services that suit customers worldwide. A standard mobile commerce transaction functions as follows.
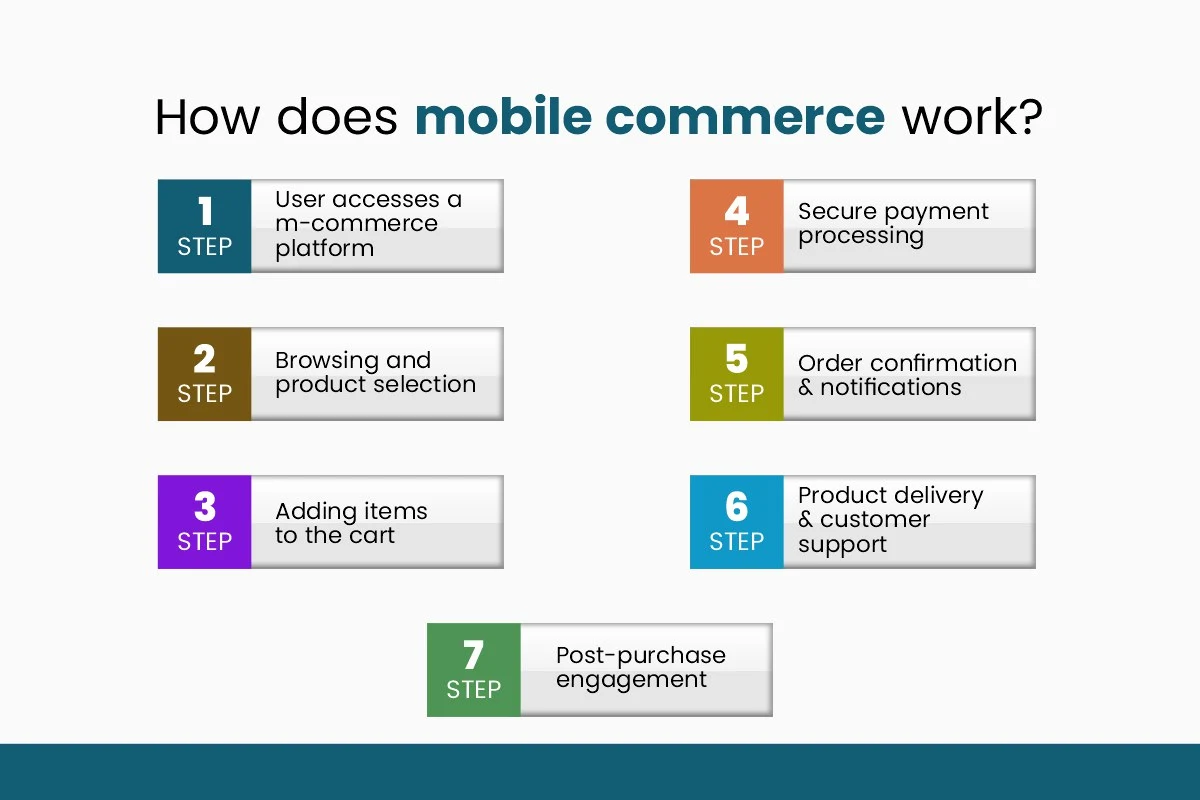
Here are the steps that normally happen during an m-commerce transaction:
Step 1: User accesses a m-commerce platform
The mobile commerce process begins as users open the mobile platform through apps or responsive websites. Sign-in authentication requires either traditional password entry with usernames or enhanced methods based on biometric authentication through fingerprint and facial identification.
A secure system in place verifies that only approved personnel possess permission to examine financial data. The platforms allow users to make single-use checkouts under the guest option to speed up their purchasing process without registering an account
Step 2: Browsing and product selection
Being logged in allows users to start their exploration of available products or services. Mobile applications use simple navigation features which include menu categories together with search tools and quick result filters.
Personalized online recommendations emerge from AI recommendations because the technology uses a user's purchasing and viewing activities to generate suggestions. The combination of good picture quality with in-depth item explanations supported by customer evaluations enables users to make their choices wisely.
Step 3: Adding items to the cart
Users can select items from their shopping carts before adding them to their online shopping carts. They can customize their orders through major platforms by changing quantities and choosing variants of colour or size. They will then receive overview details, including price subtotals with tax and delivery costs.
Users can also put their prospective purchases in the "add to cart" section of certain shopping apps to return later before making the final purchase.
Step 4: Secure payment processing
The payment process begins when users are redirected to a guarded payment gateway after finishing checkout. The secure payment process depends on encryption protocols SSL/TLS to protect sensitive information that includes both card numbers and CVVs. The platform provides different payment alternatives between credit/debit cards as well as mobile wallets (Esewa, Khalti or IME Pay) and digital banking services.
Platforms strengthen security by adding multi-factor authentication (MFA) as part of the payment process that demands three methods of verification such as password, one-time password (OTP) and biometric authentication.
Step 5: Order confirmation & notifications
Successful payment processing on the platform creates a confirmation of the order. Digital receipts get delivered to users through their email and SMS messages along with notifications within the application.
The receipt shows key information consisting of order number, product information as well as total payment amount and estimated shipping duration. Live alerts through the platform provide customers with updates concerning their orders starting with "Order Confirmed" and continuing to "Shipped" and finishing with "Out for Delivery."
Step 6: Product delivery & customer support
The logistics team receives the order for delivers it to customers. Through the application or website customers gain access to real-time shipment tracking capability. Users receive delivery notifications that show the package status to maintain full visibility.
Customers who need help will find support through chatbot help centres and direct call options that are available within the application.
Step 7: Post-purchase engagement
Mobile commerce platforms maintain continual contact with customers throughout every stage from delivery until the post-purchase period. Follow-up emails sent to customers request evaluations of their purchased products to assist additional customers in their purchase decisions.
Repeated customer visits have increased because of personalized suggestions, loyalty programs and exclusive discounts that the system offers. Push notifications within apps help notify users about new inventory selections together with sales events.
4 types of mobile commerce
The adoption of mobile commerce now lets users connect to products and services along with financial transactions by using their smartphone devices. Mobile commerce includes various daily activities which enable easier completion of tasks by users through their mobile devices.
The discussion below will explain the four main mobile commerce categories by showcasing real-life examples:
1. Mobile Shopping

Mobile shopping gives users the ability to perform product searches and assess different products as well as make purchases from their smartphone screens. Mobile commerce follows the principles of standard e-commerce and enhances these features for smartphone screens with touch functionality.
- How it Works: The mobile e-commerce system works through user access from mobile-friendly sites or applications including Daraz, Amazon, eBay, AliExpress and more. The shopping experience improves because of AI recommendations together with virtual try-on functionality and quick easy checkout capabilities.
- Example: A user starts their session on the Daraz application and quickly views wireless headphones based on reviews to finish their purchase in under five minutes through the app. Through push notifications, the system sends users tracking information about their shipments in addition to delivery updates.
2. Mobile Banking

Through the mobile banking framework, customers can perform all their financial operations outside of physical branch locations. Customers benefit from banking applications because these tools permit them to fund transfers alongside account balance viewing and loan applications.
- How it Works: Mobile banks produce safe applications for digital financial service access in real-time. Industry-leading encryption protection systems work with MFA authentication to safeguard all sensitive financial operations.
- Examples: Through their mobile banking app, customers verify their account balances, transfer funds to commerce websites and pay bills without needing to leave their residence.
3. Mobile Payments

Through smartphones, customers can securely conduct cashless transactions as a result of mobile payments. The three transactions of mobile commerce include payments done in physical stores as well as online ordering and money transfers between individuals.
- How it Works: The system connects debit or credit cards to payment solutions including eSewa, Khalti and IME Pay. Most stores accept payments through either NFC (Near Field Communication) or by using QR codes.
- Examples: Customer transactions at coffee shops are now possible using FonePay QR as users can complete payment through their phone by scanning the QR code of the shop.
4. Mobile Ticketing & Booking

The integration of mobile technology with ticket booking provides users with easy methods to book tickets for travel event attendance and entertainment activities from their mobile phones.
- How it Works: The booking procedure enables users to purchase flight tickets event passes and movie passes through their mobile apps. Digital tickets exist in mobile wallets and apps thus users can avoid using paper tickets.
- Examples: The eSewa application serves this user by letting them purchase flight services. A hassle-free check-in process occurs when the boarding pass from the phone gets scanned during the process.
What are the benefits of m-commerce?
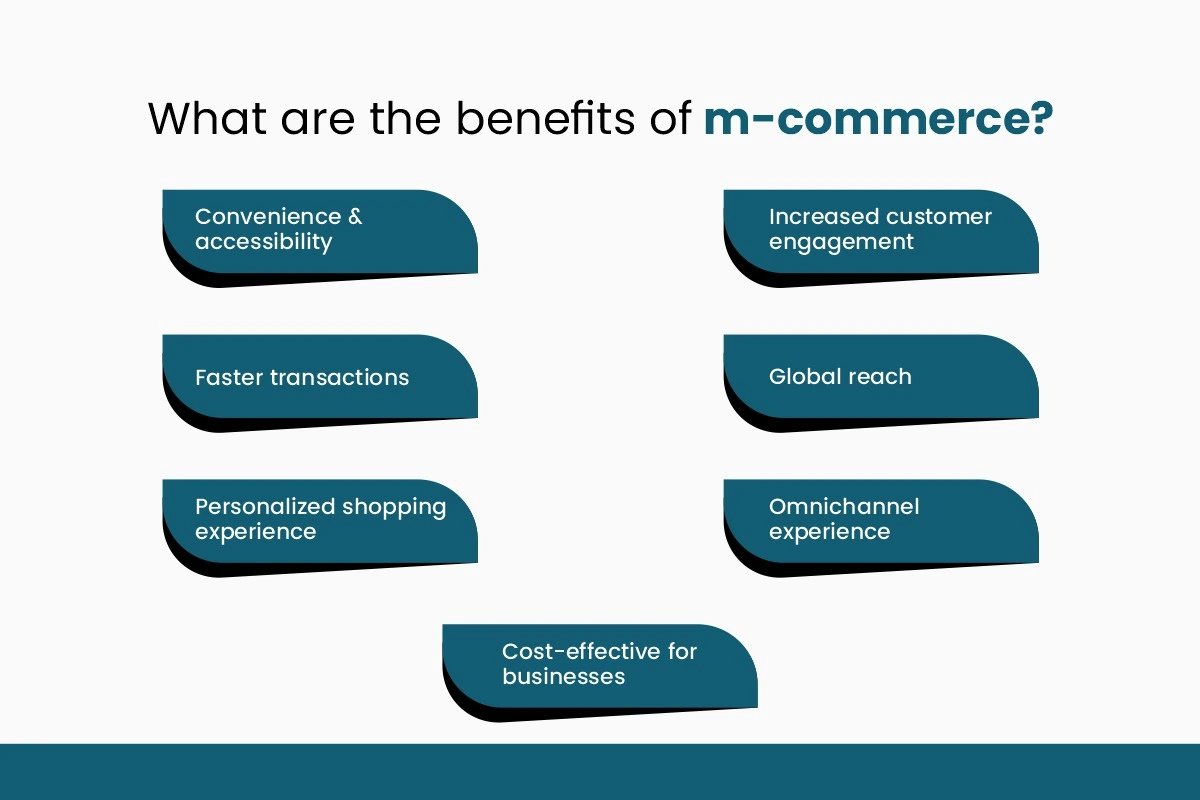
Businesses and consumers benefit extensively from mobile commerce systems because smartphone applications alongside mobile convenience create powerful advantages. Five fundamental advantages of this mobile solution deserve further examination.
- Convenience & accessibility: The modern technology of m-commerce permits users to execute shopping transactions while making bank payments and conducting payments at any time and location through their handheld smartphones.
- Faster transactions: Mobile payment solutions represented by digital wallets and one-click checkouts allow users to complete their transactions more rapidly.
- Personalized shopping experience: Mobile commerce platforms apply sophisticated algorithms to examine how customers behave and select products which helps businesses understand their preferences better.
- Increased customer engagement: Through features such as push notifications, in-app messages, and loyalty programs brands retain constant engagement from their customers.
- Global reach: Mobile commerce enables businesses to extend their reach beyond local markets. With the right platforms, companies can connect with customers worldwide, breaking geographical barriers.
- Omnichannel experience: Through the support of m-commerce businesses enable their customers to transition effortlessly between mobile apps, websites and physical locations.
- Cost-effective for businesses: Mobile platform operations eliminate the requirement for physical infrastructure together with personnel thus reducing operational expenses significantly.
What are the challenges and risks of m-commerce?
Businesses funding success in mobile commerce face multiple challenges combined with security risks that require proactive resolution for providing secure efficient services. Here are some common concerns:
- Security concerns: Mobile commerce users encounter major operational threats because of cybersecurity risks which include data breaches and attacks on identity and malware.
- Poor user experience (UX) issues: Internet applications often discourage users when they have complex navigation features, slow execution or unresponsive touchscreens.
- Connectivity & technical limitations: Every transaction under M-commerce operates based on the foundation of internet connectivity. Users experience diminished satisfaction when network coverage fails to perform in remote locations which can interrupt financial operations
- Mobile payment failures: The combination of payment processing errors together with unresponsive payment gateways which leads to declined transactions results in dissatisfied customers.
Mobile commerce trends & innovations
Technology development creates revolutionary innovations which modify consumer business interactions through mobile commerce. The following important dynamics push forward the transformation in the mobile commerce space:
1. Dominance of mobile shopping apps
Online shopping through mobile apps has become the most popular shopping method because they maintain both user-friendly design and fast access. Mobile application engagement at Daraz and Hukut expanded dramatically while users benefited from tailored suggestions membership benefits and in-app discount offers.
Mobile shopping through apps offers better convenience and betting one-button purchases making it more successful than traditional desktop e-commerce shopping.
2. AI-powered personalization
Mobile commerce experiences a revolution through Artificial Intelligence which delivers customized shopping services to users. Through artificial intelligence algorithms, businesses can review shopper activity together with past buying habits and present-time interactions to create customized merchandise suggestions alongside personalized advertising messages and adjustable pricing guidelines.
AI enables fashion retailers to offer outfit suggestions which blend past buying activities with current fashion trends.
3. Voice commerce and voice search
Voice assistants such as Alexa from Amazon, Siri from Apple together with Google Assistant have triggered the emergence of voice commerce as an upcoming retail trend. Through voice commands, customers will find their desired products then make purchases and monitor shipment progress.
The hands-free functionality serves to make products easier to access as smart house devices continue to gain popularity.
4. Mobile wallet expansion
M-commerce depends increasingly upon mobile wallet solutions provided through Apple Pay, Google Wallet and Samsung Pay. People widely adopted contactless payments after the COVID-19 outbreak began. Mobile wallets enhance operations through quick payments while connecting to loyalty programs which results in better services and security protection for customers.
5. Omnichannel shopping experiences
Customers today expect shopping convenience as they switch between channels such as mobile applications, website pages and physical stores. Through omnichannel integration, customers receive synchronized product details together with personalized promotional offers in addition to their ability to choose between multiple fulfilment options which include click-and-collect.
6. Sustainability in mobile commerce
Mobile commerce platforms maintain a commitment to sustainability because environmental considerations have gained strength. Retailers motivate sustainability through various marketing initiatives which include participating with green logistics businesses and enabling customers to measure carbon footprints.
Mobile applications like HamroBazzar have succeeded in the market through their support of secondhand shopping practices which minimize waste.
What are the tips for m-commerce success?
The highly competitive mobile commerce industry requires businesses to develop successful methods that match the current market expectations of their customers. The following methods provide direct strategies for m-commerce performance enhancement:
- Optimize for mobile-first experience: Mobile device-specific websites and application development should include responsive design quality together with straightforward navigation.
- Provide a seamless & secure checkout: The checkout process needs to be streamlined by offering one-click payments along with several payment choices that exclusively use strong security protocols.
- Personalize the shopping experience: The company should utilize data analytics along with AI technology for exchanging personalized product suggestions which combine with market-focused advertising campaigns.
- Enhance mobile app performance: Users will have improved satisfaction when application tests and optimizations happen regularly for quick performance stability and continuous operation maintenance.
- Focus on omnichannel integration: Customers should experience the same shopping environment between digital applications and website platforms as they do in physical stores through service and data integration.
- Implement fast & reliable customer support: The company should provide immediate customer support by integrating chatbots and live chats and in-app help centres for quick problem resolution.
Future of Mobile Commerce
Mobile commerce is developing fast as technological advancements have reshaped consumer interactions. The three technologies i.e. 5G connectivity, augmented reality (AR) and blockchain are enhancing the user experience in M-commerce. With the help of 5G, mobile apps can run faster, which will automatically improve customer satisfaction, while AR will transform the shopping experience by allowing virtual tours of the shop.
For example, IKEA’s AR app lets consumers see how furniture would look in their residence before their buying decision.
AI-driven chatbots and predictive analytics further enhance customer engagement, while mobile payments can be made advanced with biometrics for secure transactions. Brand sustainability will increase as brands now adopt eco-friendly practices. As mobile innovations are growing day by day brands that will adapt it faster may receive a first-mover advantage and will maintain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
The digital economy successfully operates through m-commerce because businesses can access worldwide consumers and deliver instant customer experiences with customized solutions to achieve sales objectives.
Customers now do all their shopping banking and payment transactions through mobile commerce. The digital economy functions through this technology because of its copy, fast speeds and personified features. Enterprise growth in mobile requires businesses to maintain perpetual innovation to keep up with changing consumer requirements.
FAQs
What is the difference between mobile commerce and e-commerce?
Mobile commerce (m-commerce) refers specifically to online transactions conducted through mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. E-commerce, on the other hand, includes all online transactions regardless of the device used.
How does mobile commerce impact customer behaviour?
M-commerce influences customer behaviour by offering convenience, personalization, and immediate access to products.
What is the application of m-commerce?
M-commerce is used in various sectors, including retail, banking, ticketing, and food delivery. Popular applications include mobile shopping, mobile banking apps, digital wallets, and booking platforms for travel and entertainment.
What are the most popular mobile commerce platforms?
Some of the most widely used m-commerce platforms include Amazon, eBay, Alibaba, Shopify, and Walmart. Mobile wallets like Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and PayPal also play a significant role in facilitating seamless mobile transactions.



